Mystery of GA4 attribution🤔
Introduction
Discover Google Analytics 4 (GA4), the newest version of Google's web analytics platform. With GA4, you can track and analyze user interactions on websites and mobile apps more thoroughly and flexibly. Its attribution model is an essential component for understanding user journeys and evaluating the success of marketing campaigns. In this blog, we'll explore GA4 attribution in-depth, covering key concepts, data-driven models, implementation, and practical insights for optimizing marketing efforts.
Key Concepts in Attribution
Before diving into GA4 attribution, it's essential to understand the fundamental attribution models used in analytics. There are two main categories for the GA4 attribution model.
Paid and Organic Channels
Google paid channels
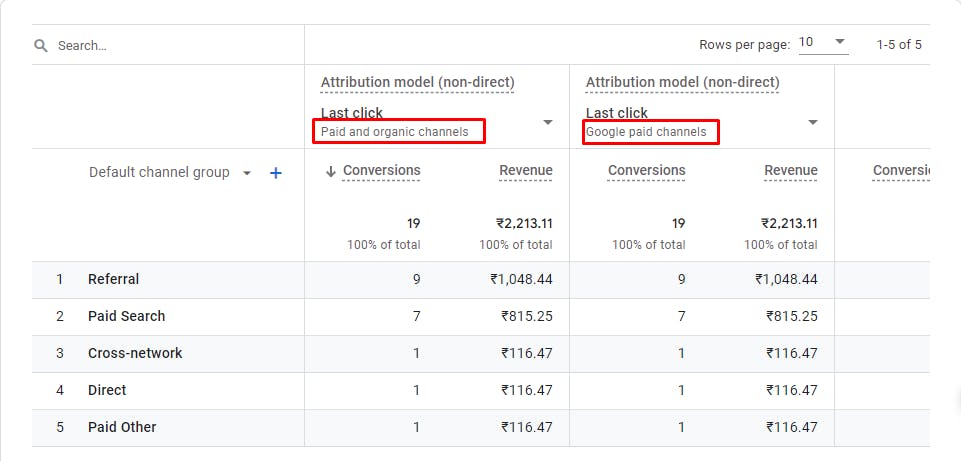
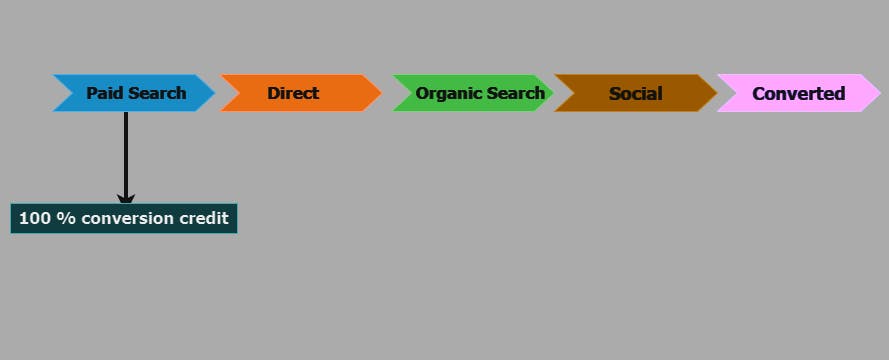
Note: Unless the entire conversion path is made up of direct visits, all attribution models will not credit conversions to direct visits.
Paid and Organic Channels
Note: The first click, linear, time decay, and position-based attribution models will be going away starting in May 2023 learn more.
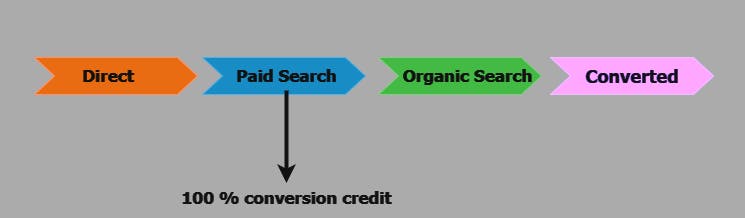
Last Click model: Attributes the conversion entirely to the last touchpoint in a user's journey.
Linear model: The linear attribution model gives equal conversion credit to all the touchpoints on the conversion path.

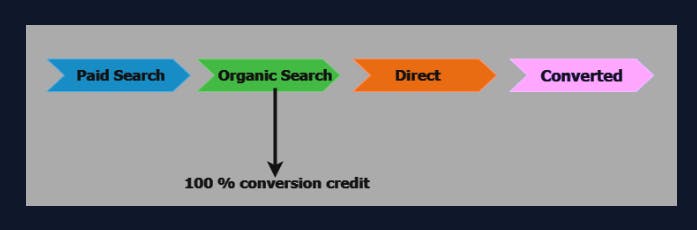
First Click model: Attributes the conversion entirely to the first touchpoint in a user's journey.
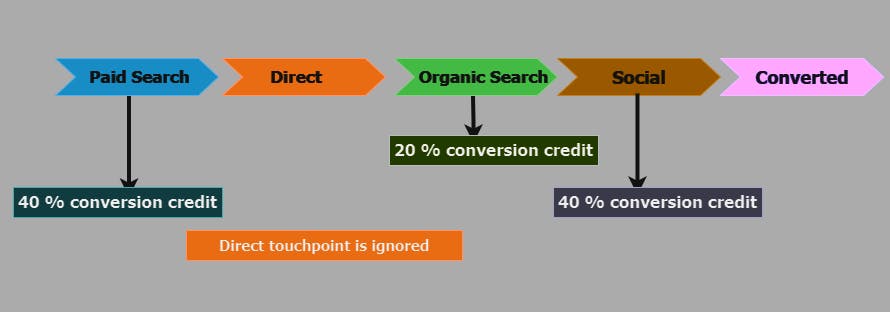
Position-based model: According to the position-based attribution model, 40% of the conversion credit is given to the first and last touchpoints on the conversion path. The remaining 20% of the conversion credit is evenly distributed among the other touchpoints on the path.
Time decay model: The time decay attribution model gives more credit to the touchpoints closer to the conversion event. The conversion credit is distributed using a 7-day half-life. So a touchpoint that occurred 8 days before a conversion gets half as much conversion credit as the touchpoint that occurred 1 day before the conversion.
Data-Driven Model: GA4's machine learning-based model that determines credit for conversions based on user behavior patterns.
Google paid channels
Last Click model: Attributes 100% of the conversion value to the last Google Ads channel that the customer clicked through before converting. If there is no Google Ads click in the path, the attribution model falls back to Paid and organic last click.

You may be thinking that you already know about these attribution models, so what makes this post special?
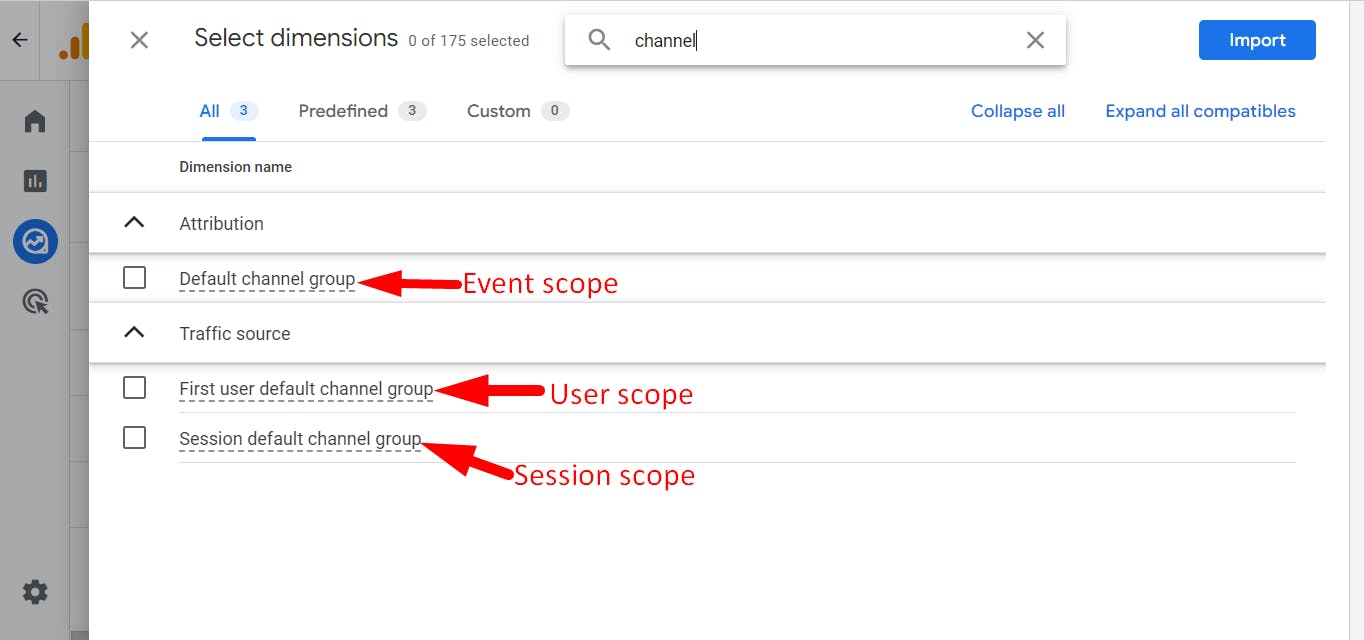
Here's the fun part, in GA4 we have 3 different scopes of dimensions.
Reporting Attribution Model
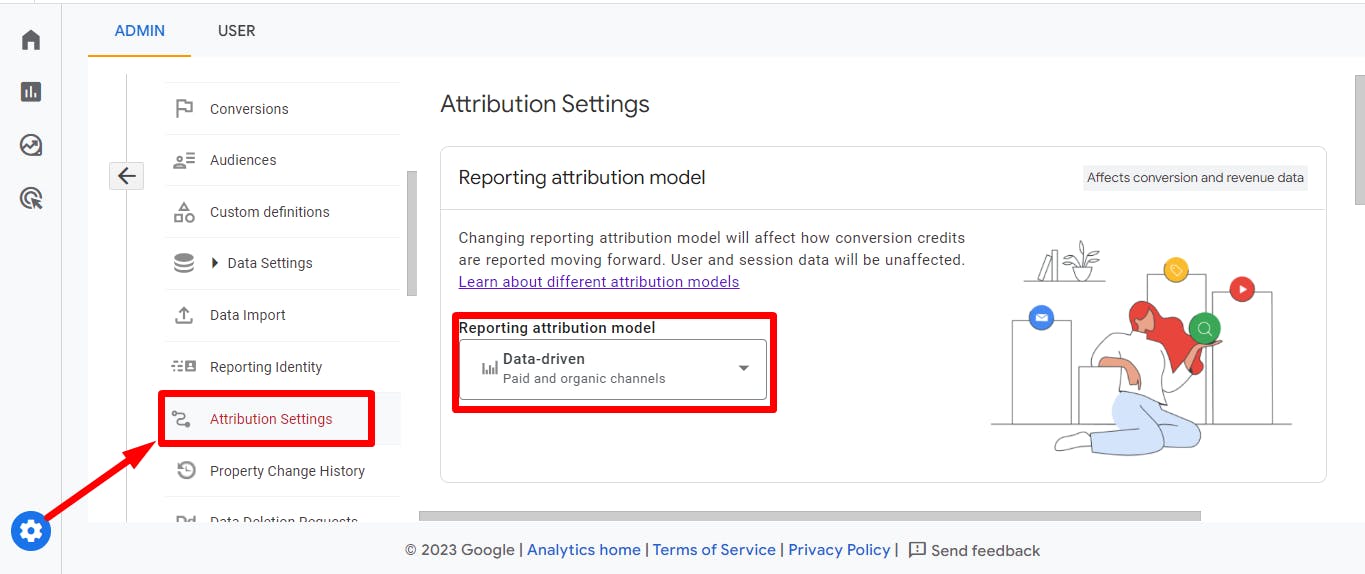
The common misconception of this setting is most of the GA4 users think reporting attribution model will reflect all the GA4 Standard and Exploration reports, which is actually not true. The Reporting attribution model only reflects the reports that use event-scope traffic dimensions (for example, Source, Medium, Campaign, and Default channel group).
User and session-scoped traffic dimensions such as Session source or First user medium are unaffected by changes to the reporting attribution model learn more.
I've noticed a glitch in the GA4 UI reporting attribution setting and reporting attribution model in a Google article, which I have discussed in a post on my LinkedIn page.
Are you interested in delving deeper into the attribution of Event, User, and Session scopes?
I'm grateful to Charles Farina for his LinkedIn posts that made the concepts easy to understand.
To gain a better understanding, let's use Sam's user journey example illustrated below.
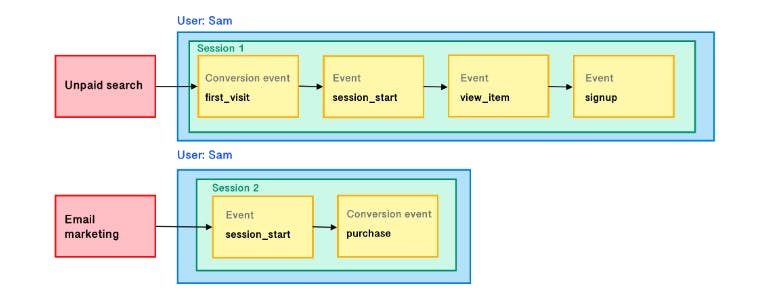
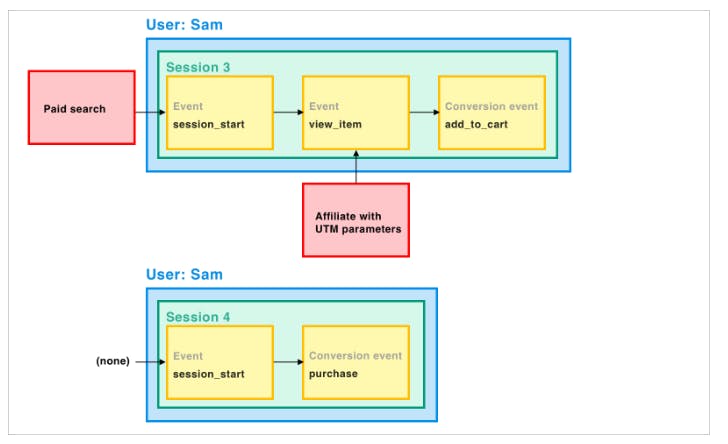
Image source: Google's article
Event Scope
Event scope dimension reports only display the converted source/medium and channels (for example, Source, Medium, Campaign, and Default channel group)**.**
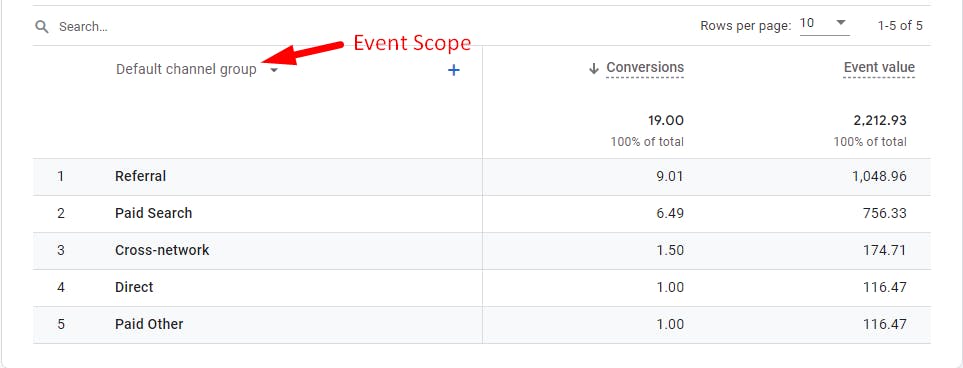
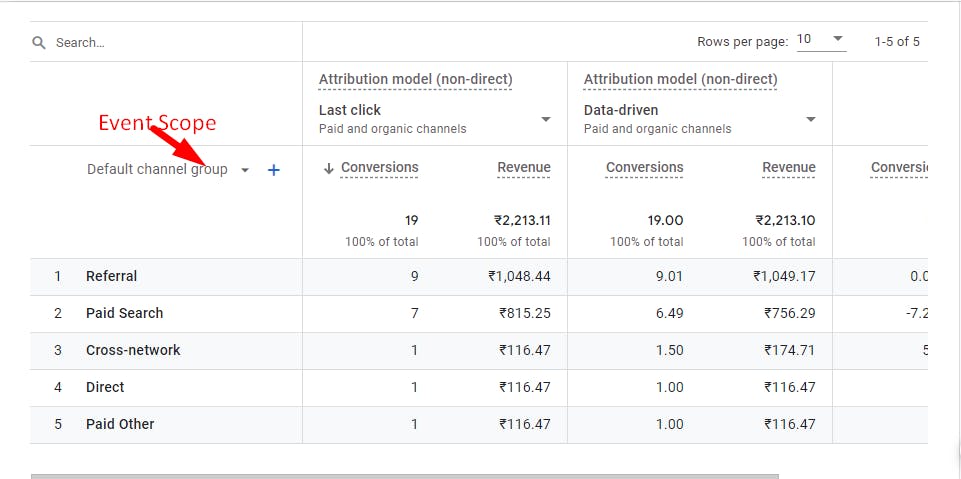
In Sam's journey mentioned earlier, The conversion count and conversion paths are defined as follows:
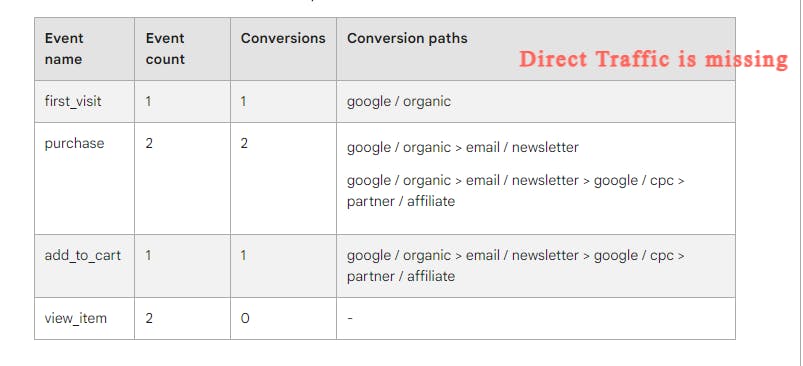
If you examine Sam's purchasing journey and its outcome closely, you will observe that the "Direct" traffic is not being credited for the conversion, even though the session was initiated by it. This is because sessions that begin with a direct entrance are attributed to the user's last known source/medium.
User Scope
User source/medium is associated with the first_visit event, so the First user source/medium is "google/organic", and it won't change for the user’s lifetime.

Session Scope
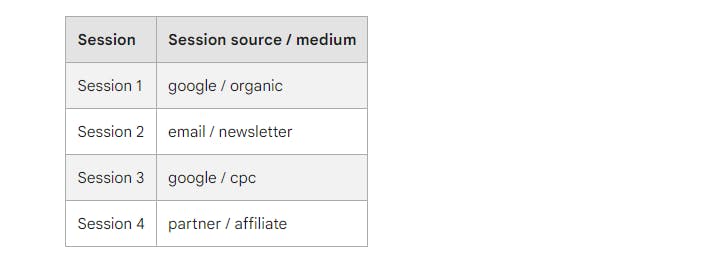
Session source/medium is assigned at the session level and represents what originated the session. Sessions initiated by direct entrance are attributed to the last known source/medium for that user. in Session scope dimensions ( session source/medium, session source, session medium) GA4 attributes the conversion to the first source/medium of the session.
When a user comes to your website through paid ads and organic channels in the same session, GA4 will only display the paid ads in the Session source/medium report.
Conclusion: At the moment, in GA4, it is not possible to determine all the traffic sources using Event, User, and Session scope dimensions as we were able to do in UA. The only solution currently available is to use BigQuery. I believe that GA4 should have one traffic dimension that would provide us with all the traffic sources. What are your thoughts on this? Please feel free to add any suggestions or comments to this post.
Sources: Article by Google.
Thank you for taking the time to read it. 🙏
If you found this article useful or enjoyable, please give it a thumbs up. 👍
Let's stay connected.👋